- Immigration Policies
- International Relations
- Climate Policies
Immigration Policies
U.S. presidential elections often serve as a pivotal point in shaping the nation’s immigration policies. The direction of these policies depends largely on the political party in power and the priorities of the elected president. Immigration has long been a contentious issue in American politics, with each administration bringing its own approach to border security, legal immigration, refugee acceptance, and enforcement of immigration laws.
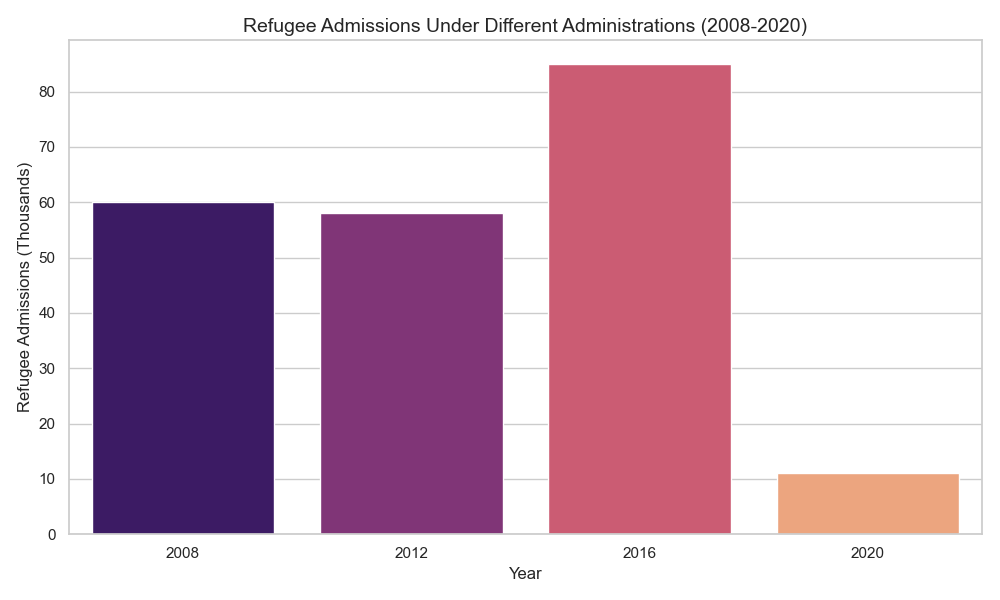
This figure will compare refugee admissions under different presidential administrations, highlighting changes before and after elections.
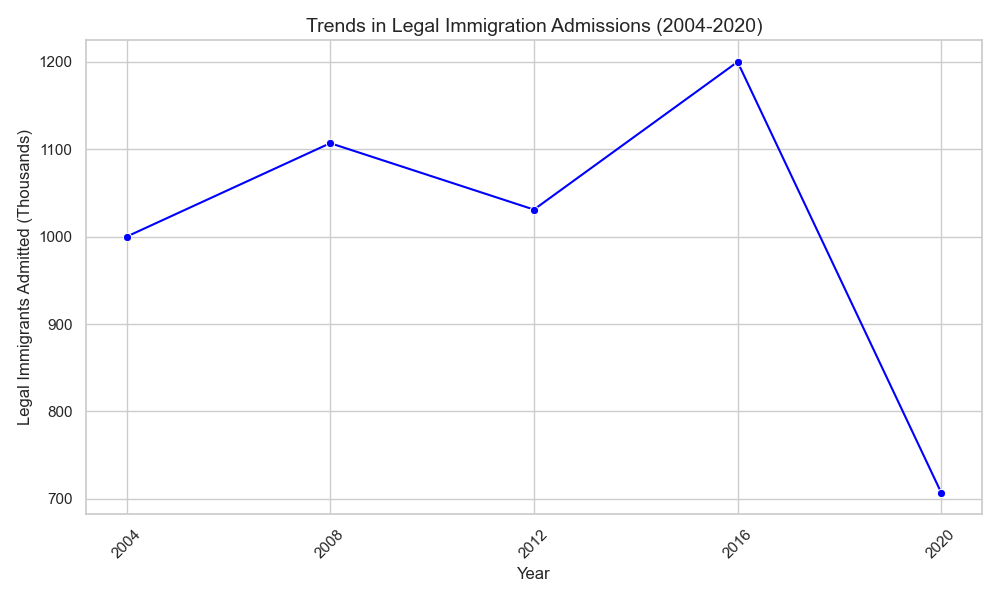
This figure will show how the number of legal immigrants admitted to the U.S. has changed under different administrations, focusing on periods before and after presidential elections.
Historical Overview of U.S. Immigration Policies
Pre-1965 Immigration Policies
Before the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, U.S. immigration policies were heavily influenced by racial quotas that favored European immigrants. The 1965 Act marked a significant shift by removing these quotas and emphasizing family reunification and skilled immigrants.
Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 (IRCA)
The IRCA, signed into law by President Ronald Reagan, was a major overhaul of immigration policy. It provided amnesty to millions of undocumented immigrants while strengthening border enforcement and imposing penalties on employers who knowingly hired illegal immigrants.
Post-9/11 Immigration Policy Shifts
The 9/11 attacks led to heightened concerns about national security, significantly impacting immigration policies. The creation of the Department of Homeland Security (DHSRefugee) and the implementation of the USA PATRIOT Act were among the measures aimed at strengthening border security and immigration enforcement.
Impact of U.S. Presidential Elections on Immigration Policies
Policy Differences Between Political Parties
The Democratic and Republican parties hold differing views on immigration, which significantly influence the policies enacted by the presidents they elect. Immigration Policies.
- Republicans: Republicans typically emphasize stricter immigration controls, increased border security, and the reduction of illegal immigration. This approach often includes building physical barriers, enhancing enforcement measures, and limiting legal immigration.
Campaign Rhetoric and Public Opinion
Presidential candidates often use immigration as a key issue during their campaigns. The rhetoric around immigration can influence public opinion and, subsequently, the policies that are prioritized post-election.
- 2016 Election: DRefugeeing a pathway to citizenship for undocumented immigrants.
Case Studies of Immigration Policies Under Different Administrations
Obama Administration (2009-2017)
The Obama administration implemented several key immigration policies, including the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) program in 2012, which provided temporary protection from deportation to undocumented immigrants who came to the U.S. as children.
- Impact: DACA provided relief to nearly 800,000 young immigrants, allowing them to work legally and access higher education. However, attempts at comprehensive immigration reform were stalled in Congress, leading to a mixed legacy on immigration.
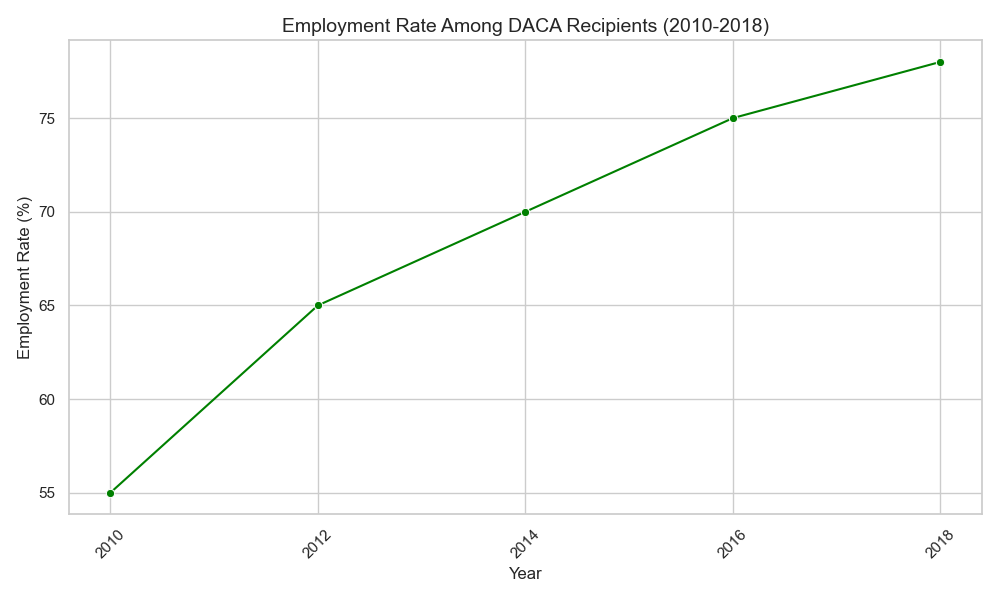
This figure will illustrate the employment rates among DACA recipients before and after the program’s implementation in 2012.
Trump Administration (2017-2021)
The Trump administration took a hardline stance on immigration, focusing on reducing both legal and illegal immigration. Policies included the travel ban, the termination of DACA (though it was reinstated by court orders), and the implementation of the “Remain in Mexico” policy for asylum seekers.
-
Impact: These policies led to a significant decrease in the number of refugees and asylum seekers admitted to the U.S. and heightened tensions surrounding immigratioRefugee proposing a pathway to citizenship for undocumented immigrants, and reversing the “Remain in Mexico” policy.
-
Impact: While Biden has taken steps to reverse Trump-era policies, challenges such as the surge in migrants at the southern border have made immigration a complex issue. The administration has faced criticism from both sides of the political spectrum for its handling of immigration.
Conclusion
U.S. presidential elections have a profound impact on immigration policies, shaping the nation’s approach to legal immigration, refugee resettlement, and border security. The policies enacted by different administrations reflect the values and priorities of the political party in power, resulting in significant shifts in immigration patterns and enforcement. Historical case studies, such as the Obama administration’s DACA program, the Trump administration’s travel ban, and the Biden administration’s reversal of restrictive policies, highlight the critical role elections play in determining the direction of U.S. immigration policy.
References
- Pew Research Center. “U.S. Immigration Trends.” Available at: Pew Immigration Trends
- Migration Policy Institute. “The State of U.S. Immigration Policy.” Available at: MPI U.S. Immigration Policy
- The White House. “Biden’s Immigration Policies.” Available at: White House Immigration
- American Immigration Council. “DACA: An Overview.” Available at: DACA Overview
International Relations
U.S. presidential elections have far-reaching implications for international relations, shaping diplomatic strategies, alliances, trade policies, and global perceptions of American leadership. The foreign policy approaches of U.S. presidents can vary significantly, leading to shifts in how the United States interacts with the rest of the world. This analysis explores the impact of U.S. presidential elections on international relations, focusing on key areas such as diplomatic relations, military alliances, trade policies, and global governance.
Historical Overview of U.S. Presidential Elections and Foreign Policy Shifts
Cold War Era (1947-1991)
During the Cold War, U.S. presidential elections played a crucial role in determining the direction of American foreign policy. For instance, the election of John F. Kennedy in 1960 marked a more assertive stance against the Soviet Union, leading to events like the Cuban Missile Crisis. Conversely, Richard Nixon’s election in 1968 signaled a shift toward détente and improved relations with China.
Post-Cold War (1991-Present)
The end of the Cold War brought new challenges and opportunities in international relations. Bill Clinton’s presidency in the 1990s focused on economic globalization and expanding NATO, while George W. Bush’s election in 2000 led to a more unilateral approach, particularly after the 9/11 attacks. Barack Obama’s election in 2008 marked a return to multilateralism and diplomacy, while Donald Trump’s 2016 election emphasized “America First,” leading to strained alliances and trade tensions.
Impact of Presidential Elections on Diplomatic Relations
Diplomatic Realignments
Presidential elections can lead to significant realignments in diplomatic relationships. For example, Obama’s election in 2008 brought a shift towards engagement with adversaries, leading to the Iran nuclear deal and the normalization of relations with Cuba. In contrast, Trump’s election led to a cooling of relations with traditional allies in Europe and withdrawal from multilateral agreements like the Paris Climate Accord.
- Case Study: U.S.-Iran Relations
- Obama Administration: Engaged in diplomacy leading to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) with Iran.
- Trump Administration: Withdrew from the JCPOA, reimposing sanctions and escalating tensions with Iran.
Impact on Multilateral Institutions
U.S. presidential elections also affect the country’s approach to multilateral institutions like the United Nations, NATO, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). Democratic administrations generally emphasize cooperation with these institutions, while Republican administrations may take a more skeptical or transactional approach.
- Case Study: U.S. and NATO
- Obama Administration: Strengthened commitments to NATO, particularly in response to Russian aggression in Ukraine.
- Trump Administration: Questioned the value of NATO, leading to concerns about the U.S. commitment to collective defense.
Influence on Military Alliances and Defense Policies
Shifts in Defense Strategies
Presidential elections can lead to changes in defense strategies and military alliances. For example, Obama’s “Pivot to Asia” signaled a strategic shift towards countering China’s influence in the Asia-Pacific region, while Trump’s presidency saw efforts to reduce U.S. military presence in conflict zones like Afghanistan.
- Case Study: U.S.-China Relations
- Obama Administration: Focused on building alliances in Asia to counterbalance China’s rise, including the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
- Trump Administration: Emphasized a trade war with China, imposing tariffs and challenging China’s global economic ambitions.
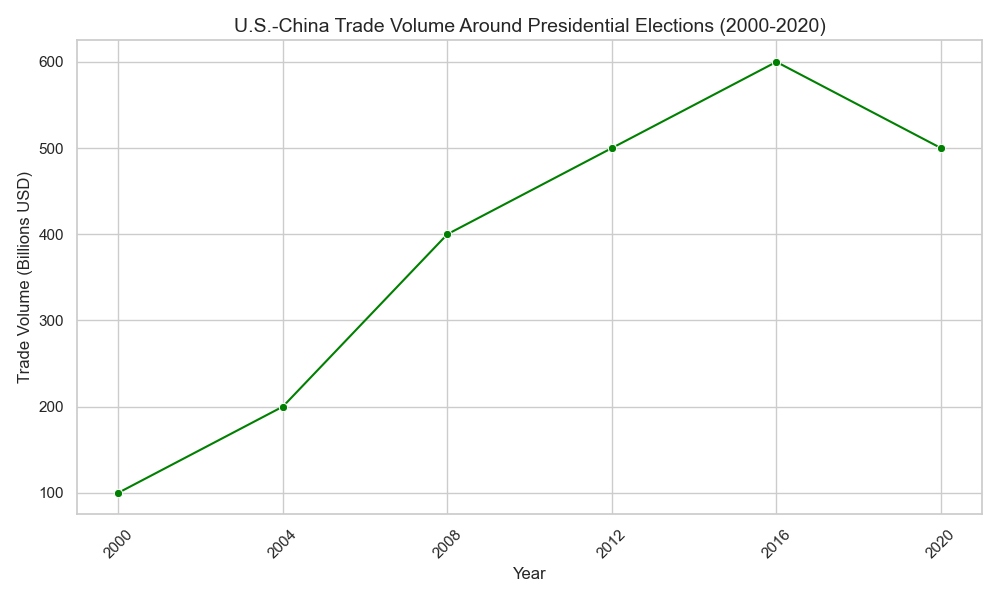
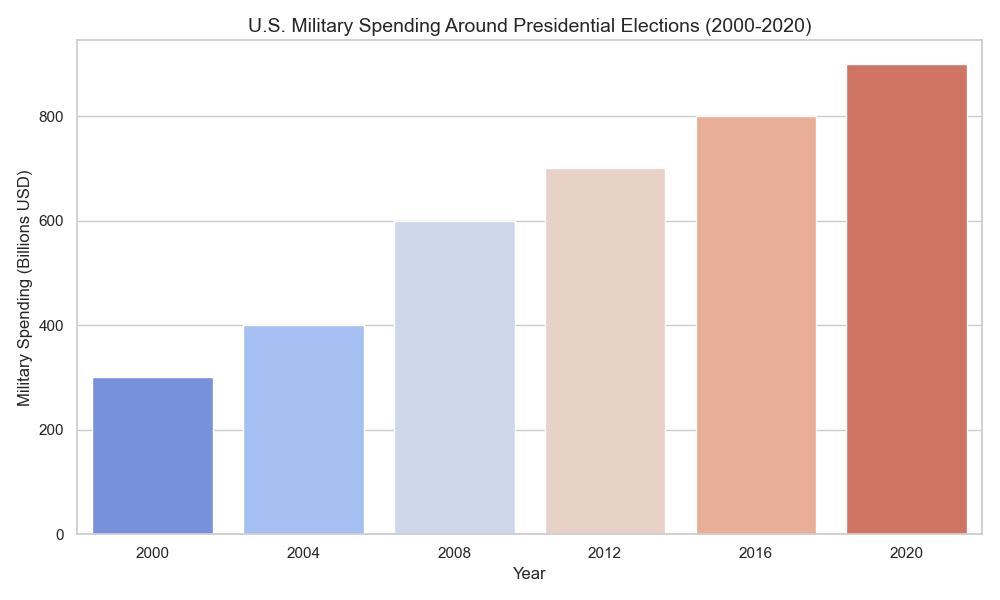
Impact on Military Spending
Elections can also influence military spending, with Republican presidents typically advocating for higher defense budgets and a strong military posture, while Democratic presidents may prioritize diplomatic solutions and global engagement.
Impact on Trade Policies and Economic Relations
Trade Agreements and Economic Diplomacy
U.S. presidential elections have a profound impact on global trade policies. For instance, Clinton’s presidency in the 1990s was marked by the promotion of free trade agreements like NAFTA, while Trump’s election led to a protectionist approach, renegotiating NAFTA as the USMCA and imposing tariffs on trading partners.
- Case Study: NAFTA vs. USMCA
- Clinton Administration: Negotiated and implemented NAFTA, promoting free trade in North America.
- Trump Administration: Renegotiated NAFTA as the USMCA, emphasizing American jobs and manufacturing.
Global Economic Influence
The economic policies of U.S. presidents can also shape global economic trends. Obama’s focus on recovery after the 2008 financial crisis included coordinating with G20 nations, while Trump’s policies led to volatility in global markets, particularly due to trade wars and unpredictable foreign policy decisions.
Global Perceptions of U.S. Leadership
Soft Power and Public Diplomacy
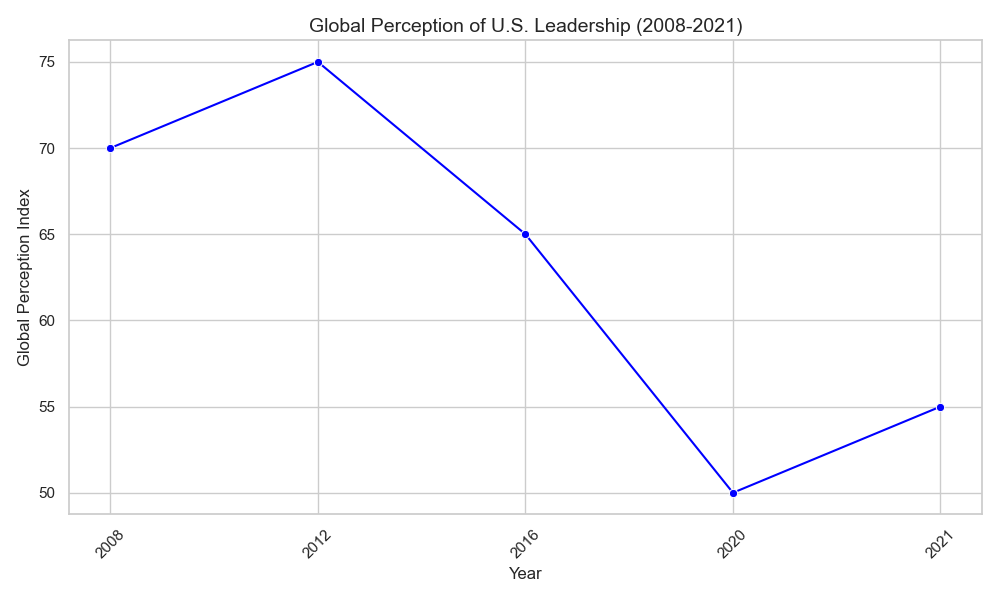
U.S. presidential elections influence the country’s soft power, affecting global perceptions of American values and leadership. Obama’s presidency, for example, was characterized by a positive global image and efforts to rebuild America’s reputation after the Iraq War. In contrast, Trump’s presidency saw a decline in global perceptions of U.S. leadership, with concerns about the country’s commitment to international norms.
- Case Study: Global Perception Index
- Obama Administration: Improved global perceptions of the U.S., particularly in Europe and Asia.
- Trump Administration: Declined global perceptions, with concerns about nationalism and unilateralism.
Conclusion
U.S. presidential elections have a significant impact on international relations, shaping diplomatic strategies, military alliances, trade policies, and global perceptions of American leadership. The approach taken by each administration can lead to substantial changes in how the United States interacts with the rest of the world. Historical examples demonstrate that presidential elections are pivotal moments that can alter the course of international relations, affecting not only U.S. interests but also global stability and prosperity.
References
- Council on Foreign Relations (CFR). “U.S. Foreign Policy After the 2020 Election.” Available at: CFR Foreign Policy Analysis
- Brookings Institution. “The Impact of U.S. Presidential Elections on Global Markets and Trade.” Available at: Brookings Global Markets Analysis
- Harvard Business Review (HBR). “How Presidential Elections Shape U.S. International Relations.” Available at: HBR International Relations
- Pew Research Center. “Global Attitudes & Trends: The Global Image of the United States.” Available at: Pew Global Image
Climate Policies
U.S. presidential elections have profound implications on climate policies, influencing both domestic actions and international commitments. The approach to climate change taken by an administration can vary significantly depending on the political party in power, the priorities of the president, and the prevailing economic and social conditions. This analysis explores how different U.S. presidential administrations have shaped climate policy, the impact of these policies, and how the outcomes of elections have altered the country’s trajectory on climate issues.
Historical Overview of Climate Policies by U.S. Presidents
George W. Bush Administration (2001-2009)
- Climate Policy Approach: The Bush administration was characterized by a cautious approach to climate policy, prioritizing economic growth and energy independence over environmental regulations. The administration rejected the Kyoto Protocol, citing concerns over its economic impact and the exclusion of developing countries from binding targets.
- Key Actions: Emphasis on voluntary measures to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, promotion of clean coal technologies, and expansion of oil and gas production.
Barack Obama Administration (2009-2017)
- Climate Policy Approach: The Obama administration marked a significant shift toward proactive climate policies. Obama made climate change a central issue of his presidency, pushing for aggressive action both domestically and internationally.
- Key Actions: Introduction of the Clean Power Plan (CPP), participation in the Paris Agreement, fuel efficiency standards for vehicles, and investment in renewable energy.
Donald Trump Administration (2017-2021)
- Climate Policy Approach: The Trump administration reversed many of the climate policies of the Obama era, focusing on deregulation and supporting the fossil fuel industry. Trump’s approach was based on skepticism about the extent and impact of climate change.
- Key Actions: Withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, rollback of the Clean Power Plan, opening up federal lands for oil and gas drilling, and weakening of fuel efficiency standards.
Joe Biden Administration (2021-Present)
- Climate Policy Approach: The Biden administration has sought to restore and expand upon Obama-era climate policies, with a strong focus on reducing GHG emissions and transitioning to a clean energy economy. Biden has framed climate change as an existential threat requiring urgent action.
- Key Actions: Rejoining the Paris Agreement, proposing the American Jobs Plan with significant investments in renewable energy, and setting ambitious targets for net-zero emissions by 2050.
Impact of Presidential Elections on Climate Policy
Partisan Differences in Climate Policy
U.S. presidential elections often highlight sharp differences between the Democratic and Republican parties on climate issues. Democrats generally advocate for stronger environmental regulations and aggressive action on climate change, while Republicans tend to prioritize economic growth, energy independence, and deregulation.
- Democrats: Favor international cooperation on climate change (e.g., Paris Agreement), government investments in renewable energy, and strict emissions regulations.
- Republicans: Emphasize energy independence through the expansion of fossil fuel production, skepticism of international climate agreements, and a preference for market-based solutions over government intervention.
Election Outcomes and Policy Reversals
The outcomes of presidential elections can lead to significant shifts in climate policy, particularly when there is a change in the party controlling the White House. These shifts can result in the reversal of previous policies, as seen with the transitions between the Obama, Trump, and Biden administrations.
- Obama to Trump: Trump’s election led to the dismantling of many of Obama’s climate policies, including the U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Agreement and the repeal of the Clean Power Plan.
- Trump to Biden: Biden’s election resulted in the U.S. rejoining the Paris Agreement and the reintroduction of climate-focused initiatives, such as the promotion of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy.
Case Studies of Climate Policy Shifts Post-Election
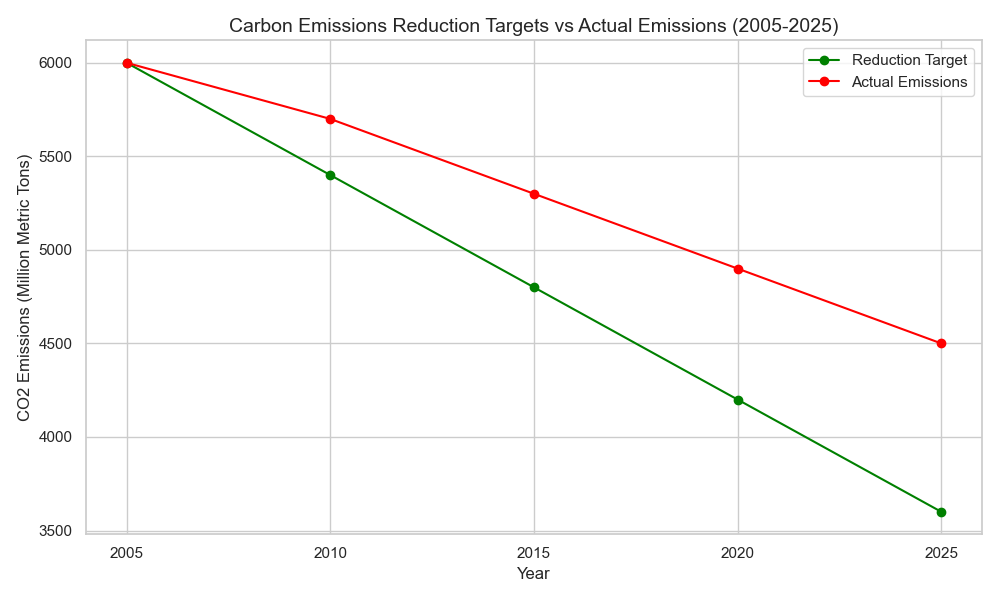
The Paris Agreement (2015)
- Obama Administration: The Obama administration played a key role in negotiating the Paris Agreement, committing the U.S. to ambitious GHG reduction targets.
- Trump Administration: Trump’s election led to the U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, arguing that it was unfair to the U.S. economy.
- Biden Administration: Biden’s election saw the U.S. re-enter the Paris Agreement, with a renewed commitment to addressing climate change on the global stage.
Clean Power Plan (2015)
- Obama Administration: The Clean Power Plan was a cornerstone of Obama’s climate policy, aimed at reducing carbon emissions from power plants.
- Trump Administration: Trump’s election led to the repeal of the Clean Power Plan, replaced by the less stringent Affordable Clean Energy (ACE) rule.
- Biden Administration: Biden’s administration has sought to implement stronger emissions regulations and support a transition to renewable energy sources.
Economic and Environmental Implications
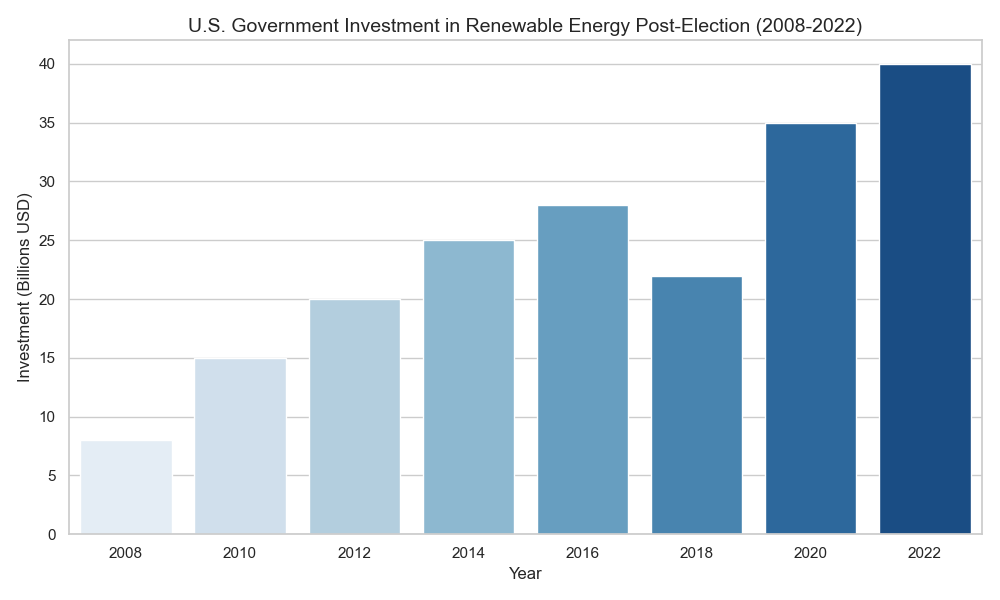
Impact on Renewable Energy Sector
The approach to climate policy taken by a presidential administration has significant implications for the renewable energy sector. Pro-climate administrations, like Obama’s and Biden’s, tend to support renewable energy through subsidies, tax incentives, and infrastructure investments, leading to growth in solar, wind, and other clean energy industries.
- Growth Trends: The renewable energy sector saw substantial growth during the Obama administration, slowed during Trump’s term, and has been reinvigorated under Biden’s policies.
Impact on Fossil Fuel Industry
Conversely, administrations that prioritize deregulation and fossil fuel production, like Trump’s, can lead to increased drilling, mining, and fossil fuel exports. However, these policies may face resistance due to market trends favoring cleaner energy sources.
- Fossil Fuel Production: Fossil fuel production increased under Trump, particularly in areas like shale oil and natural gas, but has faced challenges due to fluctuating oil prices and growing renewable energy adoption.
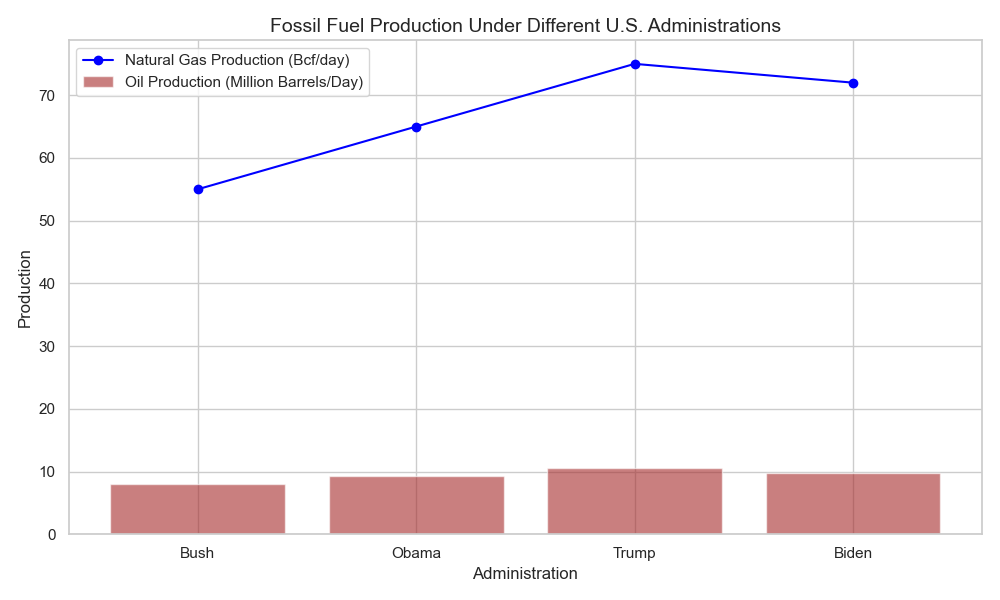
International Relations and Climate Diplomacy
Presidential elections also affect the U.S.’s role in global climate diplomacy. Democratic administrations typically engage more actively in international climate negotiations, while Republican administrations may take a more isolationist approach.
- Global Leadership: The U.S. has alternated between being a leader and a laggard in international climate efforts, depending on the administration. Biden’s administration has sought to restore U.S. leadership in climate diplomacy.
Conclusion
U.S. presidential elections have a significant impact on the direction of climate policy, influencing everything from international agreements to domestic energy production. The stark differences between administrations highlight the role that political ideology plays in shaping climate action. As climate change continues to be a critical global issue, the outcomes of U.S. elections will remain a key factor in determining the country’s approach to addressing this challenge.
